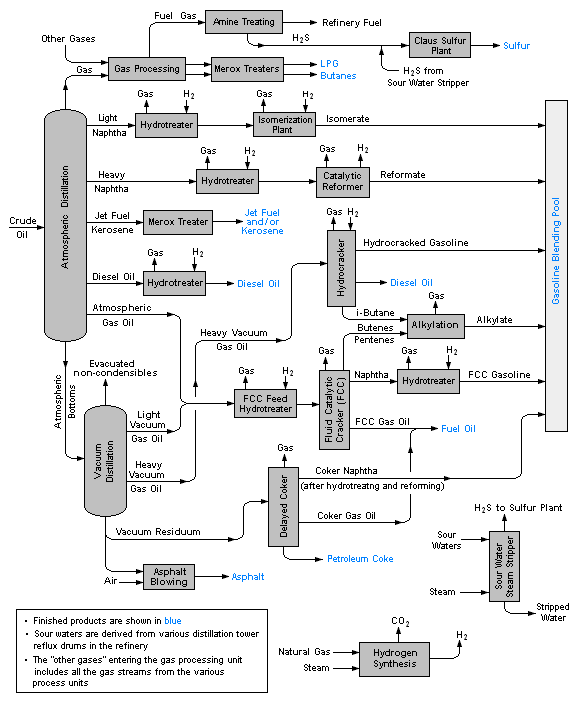
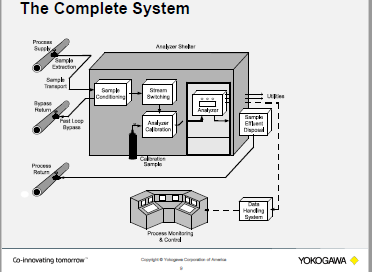
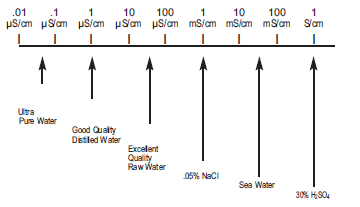
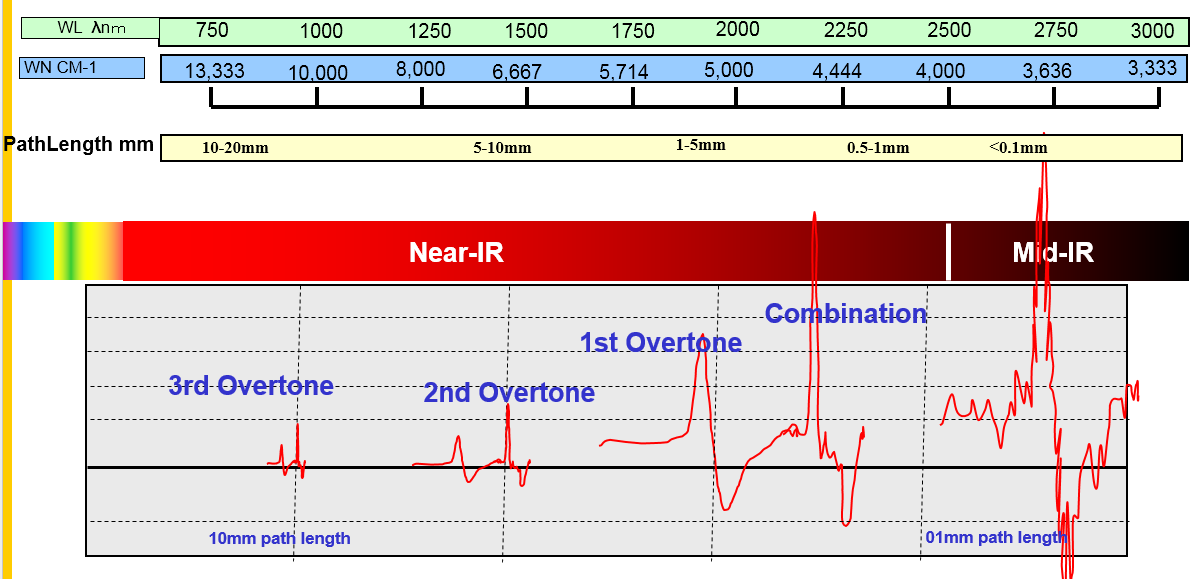
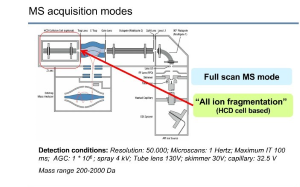
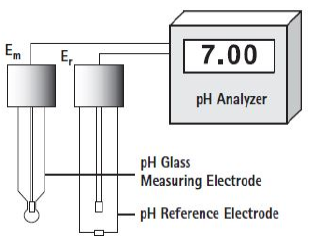
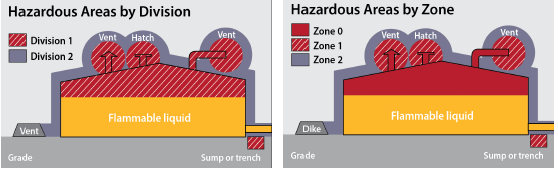
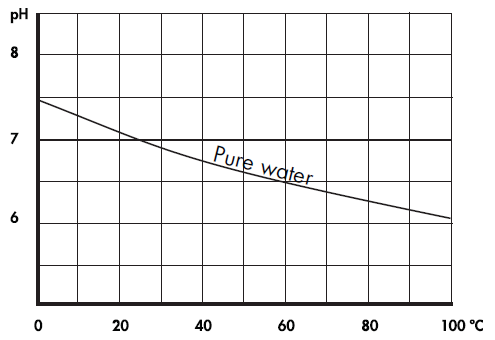
Conversion Factors - Conversion Table
By AnalyzeDetectNetwork.com sourced from Air Liquide
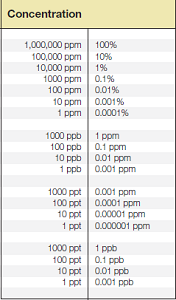
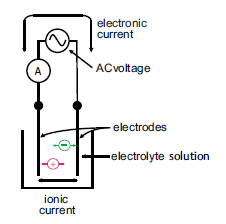
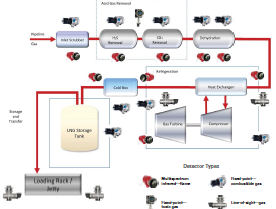
A useful conversion table, contains detailed Temperature, Weight, Density, Length, Viscosity, Velocity, Area, Thermal Conductivity, Pressure, Flow, Concentration, Dew Point conversion factors.